| 0 | abortion not permitted |
| 1 | to save a woman's life |
| 2 | to preserve physical health and to save a woman's life |
| 3 | to preserve mental health and above |
| 4 | in case of rape and incest and most of the above |
| 5 | in case of rape and incest and above |
| 6 | in case of foetal impairment and most of the above |
| 7 | in case of foetal impairment and above |
| 8 | for economic and social reasons and most of the above |
| 9 | for economic and social reasons and the above |
| 10 | on request |
| 1 | 0 to 5 |
| 2 | 5 to 10 |
| 3 | 10 to 20 |
| 4 | 20 to 30 |
| 5 | 30 to 40 |
| 6 | 40+ |
| 7 | No Data |
Links
Links
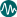
Legal Grounds for Abortion

What does it mean ?
This indicator shows the legal status of abortion in each country by categorising the grounds on which abortion is allowed into the following groups:
- abortion not permitted
- to save a woman's life
- to preserve physical health and to save a woman's life
- to preserve mental health and above
- in case of rape and incest and most of the above
- in case of rape and incest and above
- in case of foetal impairment and most of the above
- in case of foetal impairment and above
- for economic and social reasons and most of the above
- for economic and social reasons and the above
- on request
Why does it matter ?
The legal status of abortion is an important indicator of women's ability to enjoy their reproductive rights. Legal restrictions on abortion often cause high levels of illegal and unsafe abortion, and there is a proven link between unsafe abortion and maternal mortality. There is strong evidence that legal restrictions do not stop women from having abortions, driving them instead to seek unsafe and illegal procedures which risk their lives.
How is it collected ?
The UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division, Policy Section collects these data every 2 years via their World Population Policies Database.
Findings are disseminated under the website: https://esa.un.org/PopPolicy/about_database.aspx
Download their database from this website for detailed data on grounds for abortion for individual countries.
United Nations, World Population Policies Database. http://esa.un.org/poppolicy/about_database.aspx
Stillbirths in 2015
Stillbirth rate

What does it mean ?
Stillbirth rate is the number of stillbirths per 1,000 total births, which includes live births and stillbirths. A live birth refers to any baby that is born that shows signs of life outside of the womb. Stillbirths can occur before childbirth (antepartum), or during labour or childbirth (intrapartum). Stillbirths, in many cases, reflect inadequacies in antenatal care coverage or in intrapartum care. For international comparison purposes, stillbirths are defined as third trimester foetal deaths (more than or equal to 1000g, or more than or equal to 28 weeks).
Why does it matter ?
The majority of stillbirths are preventable, evidenced by the regional variation across the world. The rates correlate with access to maternal healthcare. The every newborn action plan (ENAP) to end preventable deaths has a set stillbirth target of 12 per 1000 births or less by 2030. This indicator is part of the Global Strategy for Women's, Children's and Adolescents' Health (2016-2030) under Survive: End preventable deaths.
How is it collected ?
The preferred sources for data are civil registration and vital statistics systems, and population-based surveys. Other possible data sources are administrative reporting systems, health facility assessments and special studies.
World Health Organization. 2020. Stillbirths https://www.who.int/maternal_child_adolescent/epidemiology/stillbirth/en/ [Accessed 9 March 2020]
World Health Organization. 2020. Stillbirths https://www.who.int/maternal_child_adolescent/epidemiology/stillbirth/en/ [Accessed 9 March 2020]
Stillbirth rate

What does it mean ?
Stillbirth rate is the number of stillbirths per 1,000 total births, which includes live births and stillbirths. A live birth refers to any baby that is born that shows signs of life outside of the womb. Stillbirths can occur before childbirth (antepartum), or during labour or childbirth (intrapartum). Stillbirths, in many cases, reflect inadequacies in antenatal care coverage or in intrapartum care. For international comparison purposes, stillbirths are defined as third trimester foetal deaths (more than or equal to 1000g, or more than or equal to 28 weeks).
Why does it matter ?
The majority of stillbirths are preventable, evidenced by the regional variation across the world. The rates correlate with access to maternal healthcare. The every newborn action plan (ENAP) to end preventable deaths has a set stillbirth target of 12 per 1000 births or less by 2030. This indicator is part of the Global Strategy for Women's, Children's and Adolescents' Health (2016-2030) under Survive: End preventable deaths.
How is it collected ?
The preferred sources for data are civil registration and vital statistics systems, and population-based surveys. Other possible data sources are administrative reporting systems, health facility assessments and special studies.
World Health Organization. 2020. Stillbirths https://www.who.int/maternal_child_adolescent/epidemiology/stillbirth/en/ [Accessed 9 March 2020]
World Health Organization. 2020. Stillbirths https://www.who.int/maternal_child_adolescent/epidemiology/stillbirth/en/ [Accessed 9 March 2020]