| 0 | abortion not permitted |
| 1 | to save a woman's life |
| 2 | to preserve physical health and to save a woman's life |
| 3 | to preserve mental health and above |
| 4 | in case of rape and incest and most of the above |
| 5 | in case of rape and incest and above |
| 6 | in case of foetal impairment and most of the above |
| 7 | in case of foetal impairment and above |
| 8 | for economic and social reasons and most of the above |
| 9 | for economic and social reasons and the above |
| 10 | on request |
| 1 | 0 to 5 |
| 2 | 5 to 10 |
| 3 | 10 to 20 |
| 4 | 20 to 30 |
| 5 | 30 to 40 |
| 6 | 40+ |
| 7 | No Data |
Links
Links
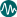
Legal Grounds for Abortion

What does it mean ?
This indicator shows the legal status of abortion in each country by categorising the grounds on which abortion is allowed into the following groups:
- abortion not permitted
- to save a woman's life
- to preserve physical health and to save a woman's life
- to preserve mental health and above
- in case of rape and incest and most of the above
- in case of rape and incest and above
- in case of foetal impairment and most of the above
- in case of foetal impairment and above
- for economic and social reasons and most of the above
- for economic and social reasons and the above
- on request
Why does it matter ?
The legal status of abortion is an important indicator of women's ability to enjoy their reproductive rights. Legal restrictions on abortion often cause high levels of illegal and unsafe abortion, and there is a proven link between unsafe abortion and maternal mortality. There is strong evidence that legal restrictions do not stop women from having abortions, driving them instead to seek unsafe and illegal procedures which risk their lives.
How is it collected ?
The UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division, Policy Section collects these data every 2 years via their World Population Policies Database.
Findings are disseminated under the website: https://esa.un.org/PopPolicy/about_database.aspx
Download their database from this website for detailed data on grounds for abortion for individual countries.
United Nations, World Population Policies Database. http://esa.un.org/poppolicy/about_database.aspx
Newborn Mortality Rate

What does it mean ?
Newborn (or neonatal) mortality rate refers to the number of deaths of newborn babies(neonates) that occur between birth and the first completed 28 days of life. It is measured as the number of deaths in the first 28 days per every 1000 live births in a given year or period. A live birth refers to any baby that is born that shows signs of life outside of the womb.
Why does it matter ?
The majority of child deaths occur in the first month of life. The newborn mortality rate provides us with a general measure of the health environment during the earliest stages of life. It is a useful indicator of the quality of care at birth in a country. Reducing newborn mortality globally forms part of Sustainable Development Goal 3.2, to end preventable deaths of newborns and children under 5 years of age.
How is it collected ?
If a country has a full birth and death registration system, then calculating Newborn (or Neonatal) Mortality Rates (NMR) is simple as all births and deaths are recorded. Where registration systems are incomplete, information on the births and deaths of babies are obtained from household surveys where women are asked about every baby they have given birth to and how long the child survived or population censuses. To calculate the mortality estimate, the data from these sources are analysed statistically using a particular model designed by the UN Inter-Agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation.
UN Inter-agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation (IGME), 2015. Median NMR estimates. http://childmortality.org/files_v20/download/RatesDeaths_AllIndicators.xlsx