| 0 | abortion not permitted |
| 1 | to save a woman's life |
| 2 | to preserve physical health and to save a woman's life |
| 3 | to preserve mental health and above |
| 4 | in case of rape and incest and most of the above |
| 5 | in case of rape and incest and above |
| 6 | in case of foetal impairment and most of the above |
| 7 | in case of foetal impairment and above |
| 8 | for economic and social reasons and most of the above |
| 9 | for economic and social reasons and the above |
| 10 | on request |
| 1 | < 5% |
| 2 | 5%-9.9% |
| 3 | 10%-14.9% |
| 4 | > 15% |
| 5 | No data |
Links
Links
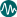
Legal Grounds for Abortion

What does it mean ?
This indicator shows the legal status of abortion in each country by categorising the grounds on which abortion is allowed into the following groups:
- abortion not permitted
- to save a woman's life
- to preserve physical health and to save a woman's life
- to preserve mental health and above
- in case of rape and incest and most of the above
- in case of rape and incest and above
- in case of foetal impairment and most of the above
- in case of foetal impairment and above
- for economic and social reasons and most of the above
- for economic and social reasons and the above
- on request
Why does it matter ?
The legal status of abortion is an important indicator of women's ability to enjoy their reproductive rights. Legal restrictions on abortion often cause high levels of illegal and unsafe abortion, and there is a proven link between unsafe abortion and maternal mortality. There is strong evidence that legal restrictions do not stop women from having abortions, driving them instead to seek unsafe and illegal procedures which risk their lives.
How is it collected ?
The UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division, Policy Section collects these data every 2 years via their World Population Policies Database.
Findings are disseminated under the website: https://esa.un.org/PopPolicy/about_database.aspx
Download their database from this website for detailed data on grounds for abortion for individual countries.
United Nations, World Population Policies Database. http://esa.un.org/poppolicy/about_database.aspx
Government Expenditure on Health in Africa

What does it mean ?
This indicator shows the level of government health expenditure relative to other government expenditures in a country. Government expenditure on health includes recurrent and capital spending by the government to improve the health status of the population and health services through public budgets, external borrowing, grants/donations and social or compulsory health insurance funds.
Why does it matter ?
Universal health coverage cannot be achieved without sufficient funds being allocated to the financing of health systems. This indicator informs us of the priority a government gives to funding health expenditures compared to other public expenditures in a country. How much a government should allocate to health expenditure depends on different factors and contexts. In 2001, Heads of State in African Union countries pledged to allocate at least 15% of their total government expenditure to health.
How is it collected ?
The preferred source of data for this indicator is a National Health Account, which is an internationally agreed method for collecting information about all financial flows related to health in a country. Where a recent National Health Account is not available, the WHO's health financing team collects similar information using technical contacts in-country and publicly available documents.
World Health Statistics 2014. http://apps.who.int/nha/database