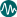
| 1 | 0 to 5 |
| 2 | 5 to 10 |
| 3 | 10 to 20 |
| 4 | 20 to 30 |
| 5 | 30 to 40 |
| 6 | 40+ |
| 7 | No Data |
| 1 | Less than 50% |
| 2 | 50% to 74% |
| 3 | 75% to 94% |
| 4 | 95% or over |
| 5 | No data |
Links
Links
Stillbirths in 2015
Stillbirth rate

What does it mean ?
Stillbirth rate is the number of stillbirths per 1,000 total births, which includes live births and stillbirths. A live birth refers to any baby that is born that shows signs of life outside of the womb. Stillbirths can occur before childbirth (antepartum), or during labour or childbirth (intrapartum). Stillbirths, in many cases, reflect inadequacies in antenatal care coverage or in intrapartum care. For international comparison purposes, stillbirths are defined as third trimester foetal deaths (more than or equal to 1000g, or more than or equal to 28 weeks).
Why does it matter ?
The majority of stillbirths are preventable, evidenced by the regional variation across the world. The rates correlate with access to maternal healthcare. The every newborn action plan (ENAP) to end preventable deaths has a set stillbirth target of 12 per 1000 births or less by 2030. This indicator is part of the Global Strategy for Women's, Children's and Adolescents' Health (2016-2030) under Survive: End preventable deaths.
How is it collected ?
The preferred sources for data are civil registration and vital statistics systems, and population-based surveys. Other possible data sources are administrative reporting systems, health facility assessments and special studies.
World Health Organization. 2020. Stillbirths https://www.who.int/maternal_child_adolescent/epidemiology/stillbirth/en/ [Accessed 9 March 2020]
World Health Organization. 2020. Stillbirths https://www.who.int/maternal_child_adolescent/epidemiology/stillbirth/en/ [Accessed 9 March 2020]
Stillbirth rate

What does it mean ?
Stillbirth rate is the number of stillbirths per 1,000 total births, which includes live births and stillbirths. A live birth refers to any baby that is born that shows signs of life outside of the womb. Stillbirths can occur before childbirth (antepartum), or during labour or childbirth (intrapartum). Stillbirths, in many cases, reflect inadequacies in antenatal care coverage or in intrapartum care. For international comparison purposes, stillbirths are defined as third trimester foetal deaths (more than or equal to 1000g, or more than or equal to 28 weeks).
Why does it matter ?
The majority of stillbirths are preventable, evidenced by the regional variation across the world. The rates correlate with access to maternal healthcare. The every newborn action plan (ENAP) to end preventable deaths has a set stillbirth target of 12 per 1000 births or less by 2030. This indicator is part of the Global Strategy for Women's, Children's and Adolescents' Health (2016-2030) under Survive: End preventable deaths.
How is it collected ?
The preferred sources for data are civil registration and vital statistics systems, and population-based surveys. Other possible data sources are administrative reporting systems, health facility assessments and special studies.
World Health Organization. 2020. Stillbirths https://www.who.int/maternal_child_adolescent/epidemiology/stillbirth/en/ [Accessed 9 March 2020]
World Health Organization. 2020. Stillbirths https://www.who.int/maternal_child_adolescent/epidemiology/stillbirth/en/ [Accessed 9 March 2020]
Women's Literacy

What does it mean ?
The adult female literacy rate is the percentage of women aged 15 and above who can, with understanding, read and write a short, simple statement.
Why does it matter ?
Improving literacy and education for women not only leads to improved health and livelihood outcomes for the woman herself and her family, but has a positive impact on a nation's economy and development. The 4th Sustainable Development Goal is to ensure inclusive and quality education for all and promote lifelong learning, with one of the stated targets being "by 2030, ensure that all youth and a substantial proportion of adults, both men and women, achieve literacy and numeracy."
How is it collected ?
Data on literacy is gathered from large scale, nationally representative surveys such as Demographic and Health (DHS) and Multiple Indicator Cluster Surveys (MICS), other national surveys and censuses.
UNESCO Institute for Statistics (June 2016 Release) based on data for 1999 - 2015 http://data.uis.unesco.org/Index.aspx?queryid=166