| 1 | More than 1 in 20 |
| 2 | 1 in 20 to 1 to 49 |
| 3 | 1 in 50 to 1 in 499 |
| 4 | 1 in 500 to 1 in 1,999 |
| 5 | 1 in 2,000 to 1 in 4,999 |
| 6 | Less than 1 in 5,000 |
| 7 | No Data |
| 0 | No Data |
| 1 | Less than 2% |
| 2 | 2-5% |
| 3 | 5-7% |
| 4 | 7-10% |
| 5 | More than 10% |
Links
Links
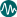
Lifetime Risk of Maternal Mortality

What does it mean ?
The Lifetime Risk of Maternal Mortality is the probability that a 15 year- old girl will die eventually from a maternal cause (any cause related to pregnancy, during childbirth, pregnancy or within 42 days of childbirth), assuming that current levels of fertility and mortality do not change during her lifetime. In high fertility societies the risk is higher because on average women go through the risk associated with pregnancy and childbirth many times in their life.
Why does it matter ?
Problems during pregnancy and childbirth are a leading cause of death and disability of women of reproductive age (15-49 years) in low income countries. This indicator acts as a marker of how likely it is to face death related to pregnancy and childbirth and reflects the ability of a country's healthcare system to provide safe care during pregnancy and childbirth.
How is it collected ?
In high income countries the data for Lifetime Risk of Maternal Mortality are from national registers of deaths to women, with maternal death as the cause. Also required in the calculation is the probability of becoming pregnant (fertility rates by age).To calculate LTR, the cumulative probability over a whole life time of becoming pregnant and dying from the pregnancy is there for calculated by summing over all reproductive ages the probabilities of becoming pregnant and dying of maternal causes
LTR 2017 - World Bank. 2020. Lifetime risk of maternal death (1 in: rate varies by country). https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SH.MMR.RISK [Accessed 9 March 2020]
Adolescent Birth Rate

What does it mean ?
This indicator represents the number of babies born to girls and women aged 15-19 each year. It can be understood as the expected number of girls that will become pregnant between the ages of 15-19 each year out of 1,000 girls in that age group.
Why does it matter ?
In countries where child marriage is common, it is also likely that a high adolescent fertility rate will result. The marriage of girls followed by multiple childbearing either in early or late teen years is a violation of human and reproductive rights, as well as a missed opportunity to improve levels of female literacy, education and the economic progress that is associated with female participation in the labour force.
How is it collected ?
A national survey was undertaken in each country from a representative sample of households where women and girls were asked how many children they have given birth to and when they occurred. Using data from girls aged 15-19, a fertility rate was calculated by adding the number of births within the year before the survey, and dividing by the number of girls in the survey aged 15-19.
World Population Prospects: The 2015 Revision https://esa.un.org/unpd/wpp/Download/Standard/Fertility/