| 1 | 0 to 5 |
| 2 | 5 to 10 |
| 3 | 10 to 20 |
| 4 | 20 to 30 |
| 5 | 30 to 40 |
| 6 | 40+ |
| 7 | No Data |
| 1 | Good vital registration |
| 2 | Alternative source |
| 3 | no nationally representative data |
Links
Links
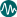
Infant Mortality Rate

What does it mean ?
The infant mortality rate is the probability that a child will die between the time of birth and exactly 1 year of age; it is expressed per every 1000 live births in that same year. A live birth refers to any baby that is born that shows signs of life outside of the womb.
Why does it matter ?
Infant Mortality Rate (IMR) was chosen as one of the indicators to be tracked as part of the targets of Millennium Development Goal 4, to reduce child mortality. It is a general indicator of child health. Rather than being an indicator that looks specifically at health care delivery it is an indicator of the socio-economic, environmental and nutritional status of children.
How is it collected ?
A preferable source of data for calculating Infant Mortality Rates is from nationally registered births and deaths. Where registration systems are incomplete, other methods are used such as household surveys where women are asked about every baby they have given birth to and how long the child survived or population censuses. To calculate the mortality estimate, the data from these sources are analysed statistically using a particular model designed by the UN Inter-Agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation.
IMR 2018 - World Bank. 2020. Mortality rate, infant (per 1,000 live births). https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.DYN.IMRT.IN [Accessed 9 March 2020]
Quality of data sources for maternal death (2015)

What does it mean ?
This indicator reflects coding for the source of maternal mortality data. As defined by the WHO, a value of '1' reflects good vital registration, '2' reflects other reliable source, and '3' reflects no nationally representative data.
Why does it matter ?
Part of the challenge in decreasing maternal mortality is accurately knowing when and where maternal deaths occur. This data is collected at the country level, with various sources of data between countries, including national vital registration, other reliable sources such as Demographic and Health Surveys, or no nationally representative data. This indicator reflects where such nationally representative data exist or don't exist. Until we know where all maternal deaths are occurring, we cannot make progress in reducing them.
How is it collected ?
These categories come from the World Health Organization's Trends in Maternal Mortality report. Group 1 indicates country estimates based on good civil registration data; Group 2 indicates modelled country estimates using available national data; and Group 3 indicates modelled country estimates where no national data are available on maternal mortality.
WHO, UNICEF, UNFPA and World Bank (2014). Trends in Maternal Mortality 1990 – 2013