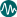
Infant Mortality Rate
Out of Pocket Health Expenditure
| 1 | 0 to 5 |
| 2 | 5 to 10 |
| 3 | 10 to 20 |
| 4 | 20 to 30 |
| 5 | 30 to 40 |
| 6 | 40+ |
| 7 | No Data |
| 1 | Less than 15% |
| 2 | 15%-29.9% |
| 3 | 30%-39.9% |
| 4 | 40%-49.9% |
| 5 | 50% and over |
| 6 | No data |
Links
Links

What does it mean ?
The infant mortality rate is the probability that a child will die between the time of birth and exactly 1 year of age; it is expressed per every 1000 live births in that same year. A live birth refers to any baby that is born that shows signs of life outside of the womb.
Why does it matter ?
Infant Mortality Rate (IMR) was chosen as one of the indicators to be tracked as part of the targets of Millennium Development Goal 4, to reduce child mortality. It is a general indicator of child health. Rather than being an indicator that looks specifically at health care delivery it is an indicator of the socio-economic, environmental and nutritional status of children.
How is it collected ?
A preferable source of data for calculating Infant Mortality Rates is from nationally registered births and deaths. Where registration systems are incomplete, other methods are used such as household surveys where women are asked about every baby they have given birth to and how long the child survived or population censuses. To calculate the mortality estimate, the data from these sources are analysed statistically using a particular model designed by the UN Inter-Agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation.
IMR 2018 - World Bank. 2020. Mortality rate, infant (per 1,000 live births). https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.DYN.IMRT.IN [Accessed 9 March 2020]

What does it mean ?
This indicator is calculated by adding together all direct payments from every household to health care providers or pharmacists, as a proportion of the total health-related spending in a country. Out of pocket health expenditure is only part of private health spending, because it does not include private health insurance. Together, government, external and private health spending make up the total health care spending in a country.
Why does it matter ?
Out of pocket health expenditure is a core indicator measuring the equity of health systems and the extent to which access to health care depends on one's ability to pay. Certain households may not be able to fund health care expenses out of pocket, resulting in untreated health problems and lack of care. For others, unplanned health spending will impoverish their whole household as they may be forced borrow money, to sell their assets or pull their children out of school to afford the costs.
How is it collected ?
The preferred source of data for this indicator is a National Health Account, which is an internationally agreed method for collecting information about all financial flows related to health in a country. Where a recent National Health Account is not available, the WHO's health financing team collects similar information using technical contacts in-country and publicly available documents.
WHO World Health Statistics 2014. Estimates for 2012 http://apps.who.int/nha/database