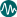
| 1 | 60% or over |
| 2 | 40% to 59% |
| 3 | 20% to 39% |
| 4 | 10% - 19% |
| 5 | less than 10% |
| 6 | No Data |
| 0 | Less than 25 |
| 1 | 25 to 49 |
| 2 | 50 to 74 |
| 3 | 75 to 99 |
| 4 | 100 to 149 |
| 5 | 150 and over |
| 6 | No Data |
Links
Links
Married Too Soon

What does it mean ?
Child marriage (also known as early marriage) is defined as a formal marriage or informal union before age 18. It is measured as the percentage of women who are in a marriage / union before the age of 18 years. It is often presented specifically for women currently aged 20-24 years only in order to give an indication of recent prevalence.
Why does it matter ?
As well as being a violation of a girl or young woman's human rights, early or child marriage is associated with curtailment of education, psychosocial disadvantage, poor reproductive health, increased risk of intimate partner violence and poor child health outcomes for the subsequent generation. The elimination of early and child marriage is a target for Sustainable Development Goal 5: toachieve gender equality and empower all women and girls. Target 5.3: "by 2030 to eliminate all harmful practices, such as early, forced and child marriage, and female genital mutilation."
How is it collected ?
In high and some middle income countries estimates are based on vital registration data. However, most estimates are based on self-reported, retrospective data from large scale, nationally representative surveys such as Demographic and Health (DHS) or Multiple Indicator Cluster Surveys (MICS). It must be noted that these surveys adopt a broad definition of marriage / union which includes legal and "traditional" marriages, as well as consensual unions with cohabitation.
UNICEF datasets most recent available data http://data.unicef.org/child-protection/child-marriage.html
Accessed 15th August 2016
A Mother Too Soon in 2015
For all too many girls around the world, pregnancy happens when they are themselves still children. However the repercussions of early motherhood can have a disastrous impact on a young woman's life. Women who give birth between the ages of 15-19 are twice as likely to die from pregnancy and birth related causes than women in their 20s, and for girls aged under 15 the risk is five times higher that women in their 20s.
Babies under one with adolescent mothers are 50% more likely to die than those with mothers in their 20s, and the younger the mother, the higher the risk.
Potential disadvantages are not just limited to health. When girls start having babies in their early teens, they miss out on school, which means they also miss opportunities to escape poverty.
As a result of unprotected sex, teenage girls are also at high risk of contracting sexually transmitted diseases including HIV. Young girls may feel unable to ask to use condoms – and in many cases they may be forced into sex. In both Malawi and Ghana around a third of girls reported that they were "not willing at all" during their first sexual experience.
Mothers under 16
In many countries girls are often married and bear their first child before the age of 16. This is particularly prevalent in Sub-Saharan Africa, but also in parts of Asia and Latin America. These very young pregnancies, which carry the greatest risks for both mother and baby, are concentrated in those countries where services are poorest.
No attribution